Hyperthyroidism refers to too much thyroid hormone in the blood coming from the thyroid gland.
What are the possible signs and symptoms of hyperthyroidism?
It can occur at any age but more often above age 10 and more often in girls than in boys. Children and adolescents may have some, but not all the typical signs and symptoms of hyperthyroidism
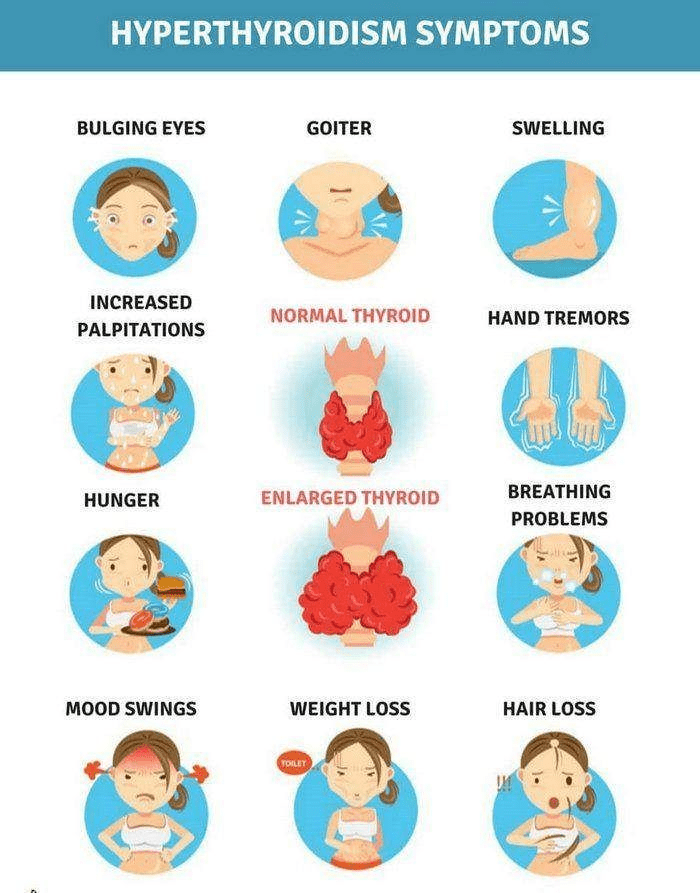
- Enlargement of the thyroid gland (goiter); usually painless
- Weight loss, despite an increased appetite
- Excessive sweating,feeling too warm when others are comfortable
- Rapid heart rate or heart palpitations
- Poor school performance
- Mood swings, difficulty sleeping,hyperactivity or restlessness
- Bulging or prominence of the eyes
- Tremors of the hands
- Increased frequency of bowel movements or diarrhoea
What causes hyperthyroidism?
In children, the most common cause of hyperthyroidism is autoimmune hyperthyroidism (Graves’ disease). The body’s immune system makes antibody proteins that stimulate the thyroid gland to make too much thyroid hormone.
Less common causes include,
- Subacute thyroiditis- A viral infection causes thyroid gland inflammation and release of preformed thyroid hormone.
- Certain thyroid swelling called toxic nodules.
How is hyperthyroidism diagnosed?
A detailed history and thorough physical examination may suggest hyperthyroidism.
The diagnosis of hyperthyroidism is confirmed by blood tests that show elevated thyroid hormone levels (total or free thyroxine [T4/FT4 ] and triiodothyronine [T3/FT3 ]) and very low thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) levels, thyroid antibodies (TPO, TGA, TRAB)
How is hyperthyroidism treated?
There are 3 main ways to treat hyperthyroidism. Antithyroid medications(tablets), radioactive iodine ablation and surgery. The choice appropriate for you will be told by your paediatric Doctor.