What are the causes of Overactive thyroid?
There are three common causes of overactive thyroid:
- Antibody mediated: Autoimmune in nature, here the antibody produced, stimulates the thyroid gland to produce more thyroid hormone.
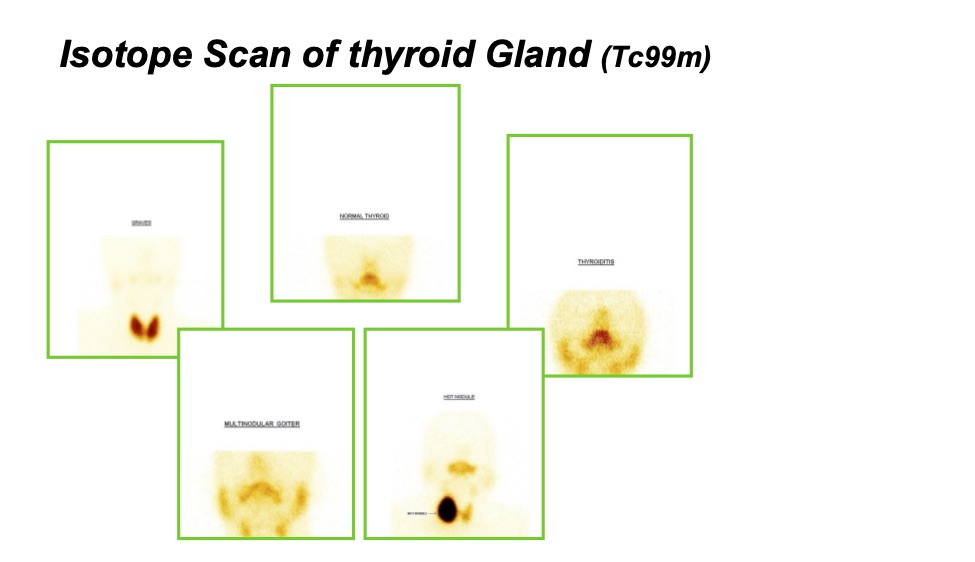
In most of the cases, the gland is big in size, this is called Graves’ disease. The name is given after the Scientist who discovered it named Sir Robert Graves’, this has nothing to do with under the ground Grave! This is mainly seen in younger people. - Toxic nodule or toxic multinodular goitre: A small area of the gland can become overactive and can start producing excess thyroid hormone. This is called toxic adenoma. If they are more than one then it is called toxic multinodular goitre. They are seen in the elderly mainly.
- Thyroiditis: The gland can get inflamed acutely called thyroiditis where the gland loses its control in keeping the thyroid hormone inside the gland. So the stored thyroid hormones come out in the blood and we develop features of an overactive thyroid.
Differentiating the reason why the thyroid is overactive makes sense as treatment of the different condition is different as the length of treatment.
How do we treat overactive thyroid?
Initial treatment
Initial treatment of overactive thyroid is always with tablets that suppress the thyroid gland (Carbimazole, Methimazole and Propylthiouracil). These drugs help prevent the thyroid from producing hormones.
They are safe but very rarely can reduce the blood count and which will make you prone for infections, particularly throat infection. So, when you develop sore throat, you should see your doctor for a complete blood count.
The rest will be done by your doctor. We also give Beta-blocker for a few weeks to control symptoms like rapid heart rate, palpitation, excess sweating by the time anti-thyroid medicines work.
Subsequent treatment
- Graves’ disease – After initial treatment with anti-thyroid medication and Propranolol (Beta-blocker) for around 6-8 weeks, we have three options
- Medical treatment – we can give antithyroid tablet in two regimen
- Titration regimen: The Antithyroid tablets given in this regime for controlling overactive gland. The dose is then tapered down to maintain your thyroid function in the normal range. Usual duration is in between 12-18 months.
- Block and replacement regimen (Antithyoid medicine in combination with Thyroxine): In this regimen we use antithyroid drugs to (block) overactive thyroid gland and thyroid hormone Thyroxine (replace). In this regimen fluctuation of thyroid balance is less common, so less number of time you need to test blood and see Doctor.
- Medical treatment – we can give antithyroid tablet in two regimen
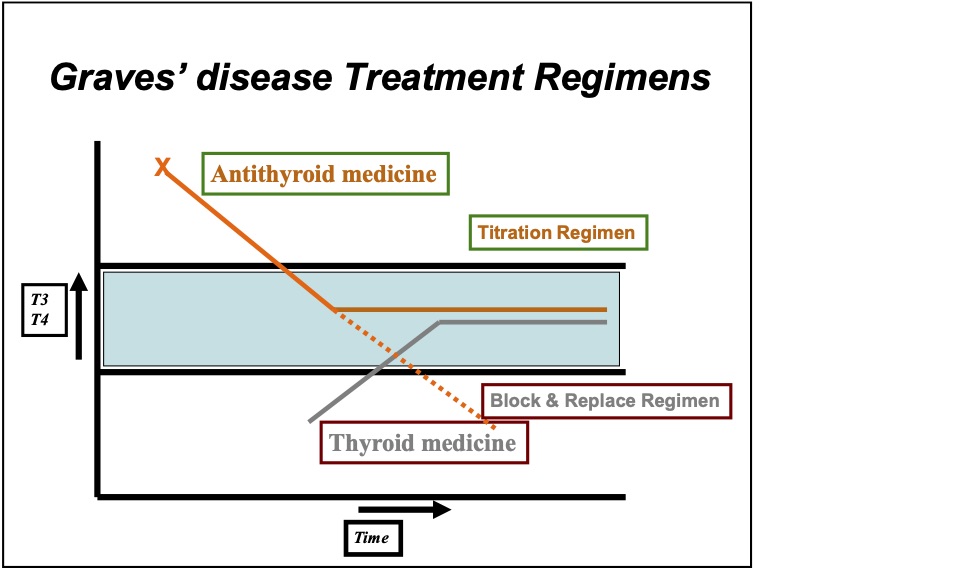
The duration of treatment is around 18 months. We then stop and see how is the thyroid behaving. If it relapses we can go for another course of medicines or radioactive iodine or surgery depending on the case.
- Radioiodine treatment – see later
- Surgery of the thyroid gland – see later
2. Thyroiditis
It is an inflammation of the thyroid gland because of which preformed hormone is released into the blood. It is usually a self limiting condition and need only symptomatic relief.
Treatment is usually Beta Blockers to control palpitations(drugs to prevent rapid heart rate).
Sometimes we do use a small dose of antithyroid medicine. It settles on its own over a time frame of 4 – 6 weeks but monitoring of thyroid function after the illness is mandatory (A Few patients have become hypothyroid and needed to be placed on thyroid hormone).
3. Toxic Nodule or toxic multi-nodular Goitre
These are the second most common cause of Hyperthyroidism after Graves’s disease. Here one or more areas of the gland form nodule which produce extra thyroid hormone.
- Initial treatment – Betablockers and antithyroid medicines are used to control symptoms and overactive thyroid gland for around 6 – 8 weeks and then we need to plan ablation therapy.
- Ablation treatment – Once overactive thyroid is reasonably controlled we need to destroy or ablate the overactive area/areas by radioiodine therapy or surgery, both has their plus and minus points. If the gland size is very big we usually prefer surgery.